The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex biological system found in all vertebrates, including humans. It plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological and cognitive processes to maintain “homeostasis”, or balance, in the body. Discovered in the early 1990s, the ECS is involved in functions such as mood, appetite, sleep, immune response, pain sensation, and memory.
Key Components of the Endocannabinoid System:
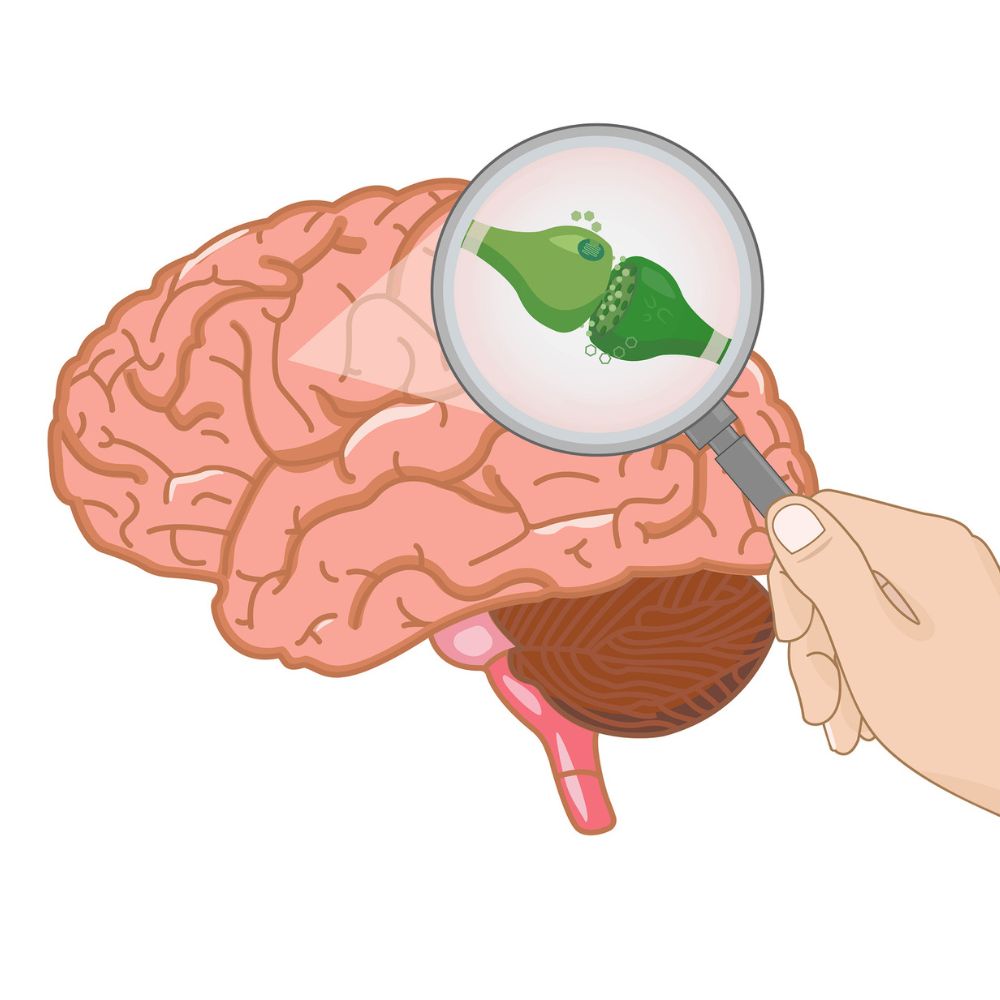
- Endocannabinoids:
- These are naturally occurring compounds produced by the body. The two main endocannabinoids are:
- Anandamide (AEA): Known as the "bliss molecule," it's involved in regulating mood, appetite, and pain.
- 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG): Plays a role in immune function and inflammation.
- Cannabinoid Receptors:
- These are proteins located on the surface of cells that endocannabinoids bind to, triggering various effects. There are two main types:
- CB1 Receptors: Found primarily in the brain and central nervous system. They influence processes like mood, memory, appetite, and pain perception.
- CB2 Receptors: Primarily located in the immune system and peripheral organs. They are involved in inflammation and immune response.
- Enzymes:
- These break down endocannabinoids once they have carried out their function. The two key enzymes are:
- Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH): Breaks down anandamide.
- Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL): Breaks down 2-AG.
How the ECS Works:
The ECS is activated when endocannabinoids bind to cannabinoid receptors, which triggers a response to help the body maintain balance. For example, if you’re stressed, the ECS might help reduce anxiety; if you’re in pain, it may help modulate the pain response.
Interaction with Cannabinoids (CBD and THC):
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol): The psychoactive component of cannabis, THC binds mainly to CB1 receptors, leading to the "high" associated with marijuana.
- CBD (Cannabidiol): Unlike THC, CBD does not directly bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors. Instead, it interacts indirectly with the ECS by influencing the activity of endocannabinoids, increasing their availability or enhancing receptor activity. This can help with conditions like pain, anxiety, and inflammation without the psychoactive effects of THC.

Functions Regulated by the ECS:
- Mood regulation
- Appetite and digestion
- Immune response
- Pain perception
- Inflammation control
- Sleep cycles
- Memory and learning
The ECS is essential for maintaining balance in many of the body's systems, and understanding its role has opened new avenues for medical treatments involving cannabinoids like CBD and THC.



Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.